(AP) — When the World Health Organization declared the coronavirus a pandemic one year ago Thursday, it did so only after weeks of resisting the term and maintaining that the highly infectious virus could still be stopped.
A year later, the U.N. agency is still struggling to keep on top of the evolving science of COVID-19, to persuade countries to abandon their nationalistic tendencies and help get vaccines where they’re needed most.
The agency made some costly missteps along the way: It advised people against wearing masks for months and asserted that COVID-19 wasn’t widely spread in the air. It also declined to publicly call out countries — particularly China — for mistakes that senior WHO officials grumbled about privately.That created some tricky politics that challenged WHO’s credibility and wedged it between two world powers, setting off vociferous Trump administration criticism that the agency is only now emerging from.
President Joe Biden’s support for WHO may provide some much-needed breathing space, but the organization still faces a monumental task ahead as it tries to project some moral authority amid a universal scramble for vaccines that is leaving billions of people unprotected.
“WHO has been a bit behind, being cautious rather than precautionary,” said Gian Luca Burci, a former WHO legal counsel now at Geneva’s Graduate Institute. “At times of panic, of a crisis and so on, maybe being more out on a limb — taking a risk — would have been better.”
WHO waved its first big warning flag on Jan. 30, 2020, by calling the outbreak an international health emergency. But many countries ignored or overlooked the warning.
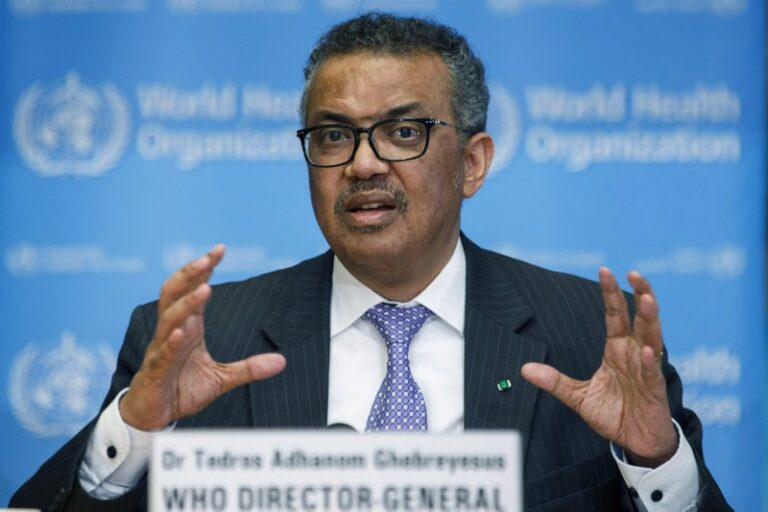
Only when WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus declared a “pandemic” six weeks later, on March 11, 2020, did most governments take action, experts said. By then, it was too late, and the virus had reached every continent except Antarctica.
A year later, WHO still appears hamstrung. A WHO-led team that traveled to China in January to investigate the origins of COVID-19 was criticized for failing to dismiss China’s fringe theory that the virus might be spread via tainted frozen seafood.
That came after WHO repeatedly lauded China last year for its speedy, transparent response — even though recordings of private meetings obtained by The Associated Press showed that top officials were frustrated at the country’s lack of cooperation.